Pharmacodynamics and Pharmacokinetics
Pharmacology is a branch of science that studies drugs and their effects on living things
Thanks to it we create the medicines that help us cure our symptoms and diseases. Did you know that a drug consists of two parts? The first is the drug which is the active substance that will act on the therapeutic target. The other part is made up of excipients which is all that surrounds the drug and helps you travel through our body until you reach the therapeutic target. An example of excipients are the soluble capsules contained in the drugs. They slowly dissolve in our stomach, gradually releasing the active ingredient so that it is absorbed in an optimal way. Thanks to it we create the medicines that help us cure our symptoms and diseases. Did you know that a drug consists of two parts? The first is the drug which is the active substance that will act on the therapeutic target. The other part is made up of excipients which is all that surrounds the drug and helps you travel through our body until you reach the therapeutic target. An example of excipients are the soluble capsules contained in the drugs. They are slowly undone in our stomachs gradually releasing the active substance so that it is absorbed in an optimal way.
In pharmacology, before studying the mechanism of action of drugs it is very important to understand two main concepts:
- Pharmacokinetics (PK)
- Pharmacodynamics (PD)
Showing 1–8 of 25 results
-
Sale!
Aceite Higea CBD 10%
29,95€ Add to cart -
Sale!
Hygea CBD Oil 20%.
49,90€ Add to cart -
Hygea CBD oil 30%.
89,95€ Add to cart -
Sale!
Aceite Higea CBD 5%
19,95€ Add to cart -
Higea CBD muscle pain cream 50 ml
21,95€ Add to cart -
Basic Pack
47,41€ Add to cart -
Medium pack
94,81€ Add to cart -
Sale!
Healing Balm Hygea CBD
19,95€ Add to cart
What is pharmacokinetics?
Its etymology comes from Greek and refers to the movement of drugs. Broadly speaking pharmacokinetics is what the body does with drugs. Describes the absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion of compounds. This is why many times when we go to the doctor and are prescribed a medicine always ask us some questions that aim to detect if there is any of our inner workings that can affect the pharmacokinetics of the drug we are going to take. For example, if we have kidney, liver or circulation problems that will interfere with the normal circulation of the drug through our body.
Therefore, when we talk about pharmacokinetics, we focus on the study of the entry and exit of the drug into our body.
The input:
When a substance enters it is important to know which way it enters and at what speed. The most common routes of administration are oral and intravenous. After knowing which way the drug has entered and how fast, i.e. we know its bioavailability,we can proceed with the study of its absorption. Absorption comprises the process during which the compound travels from the route of administration to the plasma. As a last process of entry it is important to know how the drug is distributed through our body.
The output:
Once the drug has been absorbed and distributed we are interested in knowing how it leaves the body. The elimination of the compounds can be by biotransformation, i.e. by the body transforming them or by excretion.
What is pharmacodynamics or pharmacodynamics?
For its etymology also Greek refers to the potency of drugs. That is, the study of what the drug does to our body. Once the drug reaches the therapeutic target it will have to interact with cell receptors to cause an effect on cells.
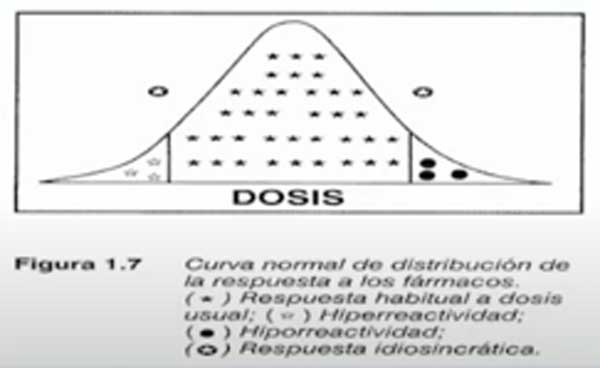
Each individual has a different response to drugs. However, the statistical distribution of the response to the drugs of the population is a normal (or Gaussian bell). In this distribution we will find a mean in the center of the hood, extreme cases of hyporeactivity or hyperreactivity at the ends of the curve and also idiosyncratic cases that are outside the curve.
In addition, if the drug is administered repeatedly and it is necessary to increase the dose, it is said to generate tolerance. The more we have to increase the dosage to get the desired effects the more tolerant and dependent the drug becomes the individual.
The study of the side effects of drugs corresponds to the branch of pharmacodynamics. Even if side effects are not adverse, it is crucial to know them. For example, if we are going to drive it is better not to take antihistamines that have a drowsiness effect. This one wouldn’t be adverse if instead of driving we want to fall asleep at night.

Pharmacodynamic tolerance
Pharmacodynamics also studies drug interactions. There are synergy relationships in which the effects of one or both drugs increase or enhance. The drug-drug facilitation effect is also widely used in pharmacology. In these cases the effects of one of the drugs facilitate the action of the other. For example, clabulamic acid is used in conjunction with penicillin to prevent bacteria from generating antibiotic resistance.
The study of the dose in pharmacodynamics is important to determine the therapeutic and safety margins of each drug,to know from which dose the drug will have effect on the individual and from what dose it can be lethal. Thanks to the dose curves – response we can know how each dose behaves.

Pharmacodynamic interaction
Pharmacodynamics also includes the analysis of the mechanisms by which drugs act in our body. Drugs can act on target molecules such as proteins (enzymes, ion channels, transport molecules or receptors); DNA ; or silent joints (plasma proteins or specific binding). In addition, there are drugs that do not act on target molecules. For example, when we feel acidity and take an antacid it will not act on a target molecule, but will directly change the PH of our stomach to neutralize the acids.
The most common interactions in pharmacodynamics are with receptors. These are macromolecules that receive stimuli and transmit them to cells to generate an effect. Drugs can act selectively to modify a specific function of the cell where they are acting. In pharmacology the analogy of the lock (the receiver) and the key (the drug) is widely used. If the ligando is agonist it means that the lock will open the door to hormones or neurotransmitters. If he is antagonistic, he will act by closing and locking the door.

Depending on the type of chemical bond between the receptor and the ligando (the drug) there will be passenger or more lasting effects. The weaker the binding (e.g. a Van der Waal bridge) the more transient the effect of the drug will be. However, if covalent type joints occur (not common) they are permanent bonds with irreversible cell changes. In this case the receptor would be unused for life and forcing the body to produce a new receptor.
When introducing a drug or substance into our body it is essential to know how our body will treat it (pharmacokinetics) and also what effects it will have on our body (pharmacodynamics). Although the population study concludes in a normal distribution, each individual is a world and that is why our idiosyncratic characteristics can affect the dosage we should take to achieve the least adverse side effects and the greatest therapeutic efficacy. It must be a specialist who examines your case and prescribes the dose and medications needed to treat you.
Related articles
CBD and contraceptives
CBD and contraceptives. We explain what they are, and which are the most common pregnancy prevention methods Enter!
Tantric exercises to improve your sexuality
Tantra is a complex and ancient practice with a wide range of techniques. Can be used to enhance sexual experiences
Gifts for people with anxiety
When it comes to selecting gifts for people with anxiety, it is important to keep in mind that everyone's experiences and coping mechanisms are different. However, in this article we share with you some gift ideas that can be beneficial for people with anxiety.What...
CBD for studying
Did you know that you can use CBD to study and improve your academic performance? Enter to find out how CBD helps you study better!
Is CBD oil safe during pregnancy and breastfeeding?
Pregnancy and breastfeeding are very delicate times for the health of mother and baby, so many substances are not compatible with the process. If this is your case and you are not sure about the effects that CBD oil can have on your body, you should know this...
What is Bisabolol, and what are its benefits?
Bisabolol, a cannabinoid that despite being little known, is known to have enormous medicinal potential Enter now!
Subscribe to our newsletter
Subscribe and receive a 10% discount on your purchase.
Store
Categories
Guides
Legal notice and privacy policy